Refer To The Diagram To The Right The Vertical Difference Between Curves F And G Measures
Curve g approaches curve f because 22 a fixed cost falls as capacity rises. 21 refer to figure 11 5.
8 refer to figure 10 4.

Refer to the diagram to the right the vertical difference between curves f and g measures. H average fixed cost curve. The vertical difference between curves f and g measures a average fixed costs. B could occur because of an influx of immigrant labor.
28 the vertical difference between curves f and g measures a average fixed costs. Refer to figure 11 5. B total cost falls as more and more is produced.
If the average variable cost curve is above the marginal cost curve then 86. C fixed cost falls as capacity rises. 29 curve g approaches curve f because a marginal cost is above average variable costs.
The vertical difference between curves f and g measures 84. If average total cost is 50 and average fixed cost is 15 when output is 20 units then the firms total variable cost at that level of output is. The vertical difference between curves f and g measures a average fixed costs.
The vertical difference between curves f and g measures average fixed costs. Refer to figure 11 5. C average fixed costs.
G average variable cost curve. F average total cost curve. 18 refer to figure 10 4.
D e marginal cost curve. A movement from x to y a could be due to a change in consumers tastes and preferences. Refer to figure 1.
The vertical difference between curves f and g measures 21 a marginal costs. The vertical difference between curves f and g measures a average fixed costs. 19 the abc company manufactures routers that are used to provide high speed internet service.
22 refer to figure 11 5. If the marginal cost curve is below the average variable cost curve then 85. Refer to the diagram to the right.
The vertical difference between curves f and g measures marginal costs.
 What Shifts Aggregate Demand And Supply Ap Macroeconomics Revie
What Shifts Aggregate Demand And Supply Ap Macroeconomics Revie
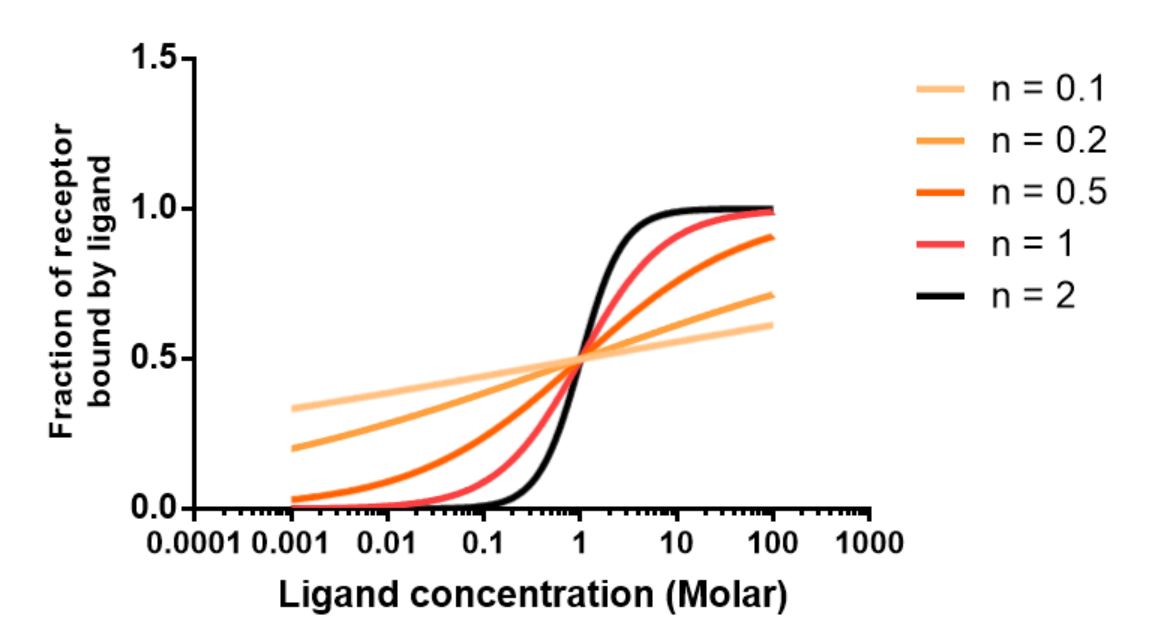 Hill Equation Biochemistry Wikipedia
Hill Equation Biochemistry Wikipedia
 Forming Limit Diagram An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Forming Limit Diagram An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 3 6 Equilibrium And Market Surplus Principles Of
3 6 Equilibrium And Market Surplus Principles Of
Experiments In Physics Physics 1291 General Physics I Lab
 Function Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica Com
Function Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica Com
 Phase Difference And Phase Shift In An Ac Circuit
Phase Difference And Phase Shift In An Ac Circuit
Osa Optical Anisotropy Of Non Perturbative High Order
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/PPCEnhanced-5b37b9cc46e0fb0037f491eb.jpg) Production Possibilities Curve Explained With Examples
Production Possibilities Curve Explained With Examples

 The Economy Leibniz Isoprofit Curves And Their Slopes
The Economy Leibniz Isoprofit Curves And Their Slopes
Calculus I Area Between Curves
 Intro To Signal Processing Integration And Peak Area Measurment
Intro To Signal Processing Integration And Peak Area Measurment
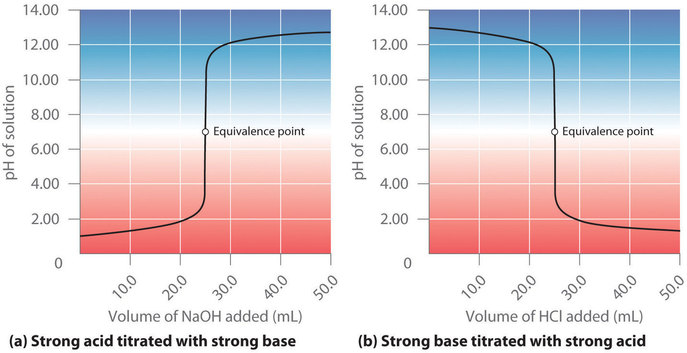 17 4 Titrations And Ph Curves Chemistry Libretexts
17 4 Titrations And Ph Curves Chemistry Libretexts
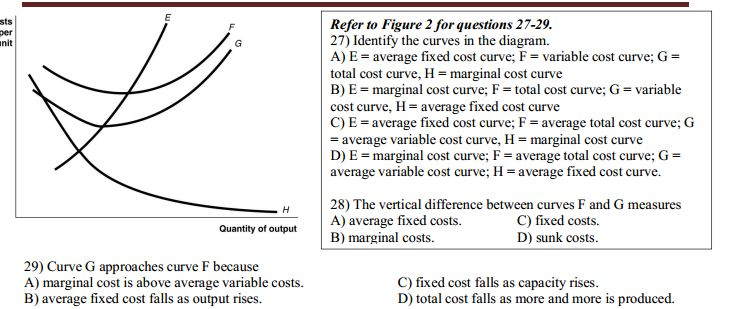 Solved Curve G Approaches Curve F Because Marginal Cost I
Solved Curve G Approaches Curve F Because Marginal Cost I

 Youden Index An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Youden Index An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

 Esd Downslope Windstorms In The Isthmus Of Tehuantepec
Esd Downslope Windstorms In The Isthmus Of Tehuantepec
Calculus I Area Between Curves
Volume With Cross Sections Squares And Rectangles No Graph
Graphing Rational Functions 3 Video Khan Academy
 Differential Regulation Of Oct4 Targets Facilitates
Differential Regulation Of Oct4 Targets Facilitates
2 Area Under A Curve By Integration
 The Economy Leibniz Isoprofit Curves And Their Slopes
The Economy Leibniz Isoprofit Curves And Their Slopes
2d Plotting Sage Reference Manual V8 9 2d Graphics


0 Response to "Refer To The Diagram To The Right The Vertical Difference Between Curves F And G Measures"
Post a Comment