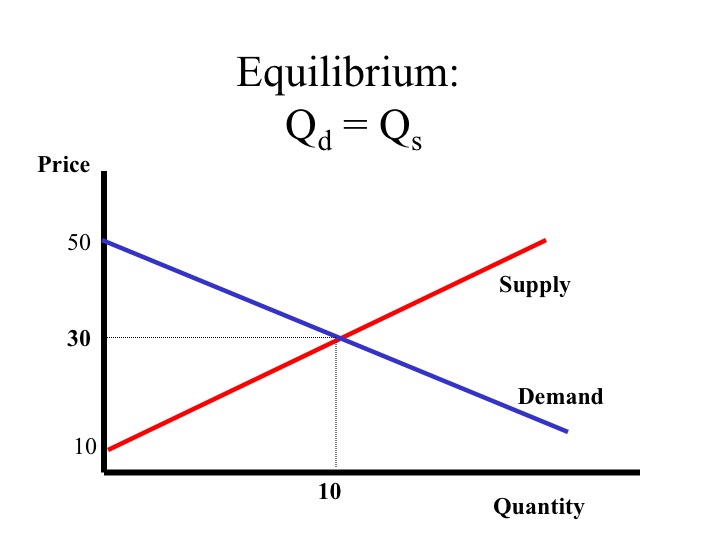
On A Supply And Demand Diagram Quantity Demanded Equals Quantity Supplied
Four laws of supply and demand. In microeconomics supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a marketit postulates that holding all else equal in a competitive market the unit price for a particular good or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded at the current price will equal the quantity supplied at the.
Segment 4 Pricing In Mass Markets
The price that makes quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied is called the equili b rium price.

On a supply and demand diagram quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The equilibrium price is the only price where the desires of consumers and the desires of producers agreethat is where the amount of the product that consumers want to buy quantity demanded is equal to the amount producers want to sell quantity supplied. At a price above the equilibrium price there is. We may now refer to the following four laws of supply and demand.
A leftward shifts refers to a decrease in demand or supply. On a supply and demand diagram equilibrium is found 29. The following graph illustrates an increase in supply and an increase in quantity demanded.
The is the quantity where quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal at a certain price. It occurs where the demand and supply curves intersect. On a supply and demand diagram quantity demanded equals quantity supplied a.
On a supply and demand diagram quantity demanded equals quantity supplied true a surplus will occur in a market when the price of the product is above the equilibrium price. Demand versus quantity demanded and supply versus quantity supplied. The implication is that a larger quantity is demanded or supplied at each market price.
Only at the single equilibrium price. The equilibrium price for dog treats is the point where the demand and supply curve intersect corresponds to a price of 200. This mutually desired amount is called the equilibrium quantity.
On a supply and demand diagram quantity demanded equals quantity supplied only at the single equilibrium price. It means that less is demanded or supplied at each price. Quantity produced equilibrium quantity demand schedule supply schedule question 5 3 out of 3 points the nature of demand indicates that as the price of a good increases.
The above diagram illustrates that supply increases as s1 shifts to s2 and quantity demanded increases as the equilibrium point shifts along the demand curve. Buyers desire to purchase less of it.

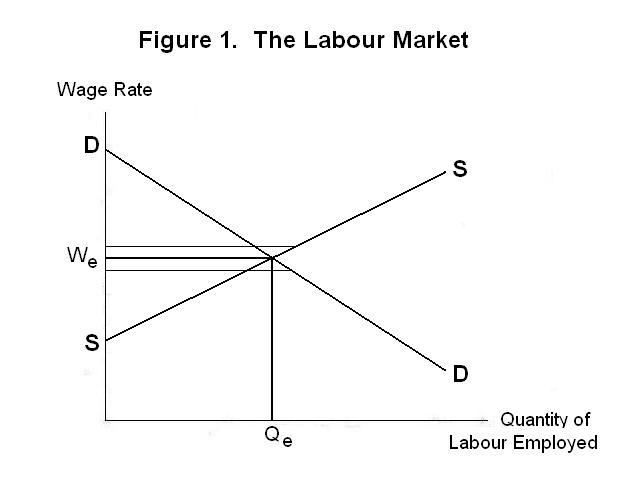 Wage Rates And The Supply And Demand For Labour
Wage Rates And The Supply And Demand For Labour
 Calculating Equilibrium Price Definition Equation
Calculating Equilibrium Price Definition Equation
 Market Equilibrium Microeconomics Assignment
Market Equilibrium Microeconomics Assignment
 Change In Demand Versus Change In Quantity Demanded
Change In Demand Versus Change In Quantity Demanded
Economics Storybook Storyboard By Reileys
 3 6 Equilibrium And Market Surplus Principles Of
3 6 Equilibrium And Market Surplus Principles Of
Lesson Plan Demand Supply And Market Equilibrium Ppt
Shifts In Demand And Supply With Diagram
 Solved The Diagram To The Right Is A Basic Supply And Dem
Solved The Diagram To The Right Is A Basic Supply And Dem
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/g367-5c79c858c9e77c0001d19d1d.jpg) Illustrated Guide To The Supply And Demand Equilibrium
Illustrated Guide To The Supply And Demand Equilibrium
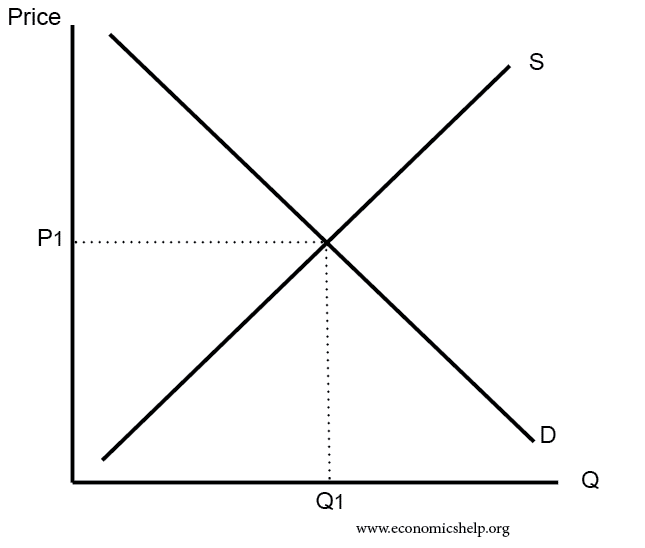 Diagrams For Supply And Demand Economics Help
Diagrams For Supply And Demand Economics Help

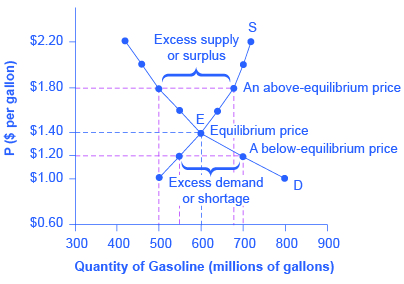 Reading Equilibrium Where Demand And Supply Intersect
Reading Equilibrium Where Demand And Supply Intersect
Econ 200 Introduction To Microeconomics Homework 3 Part Ii

Why You Should Never Use A Supply And Demand Diagram For
 Markets Equilibrium Economics Online
Markets Equilibrium Economics Online
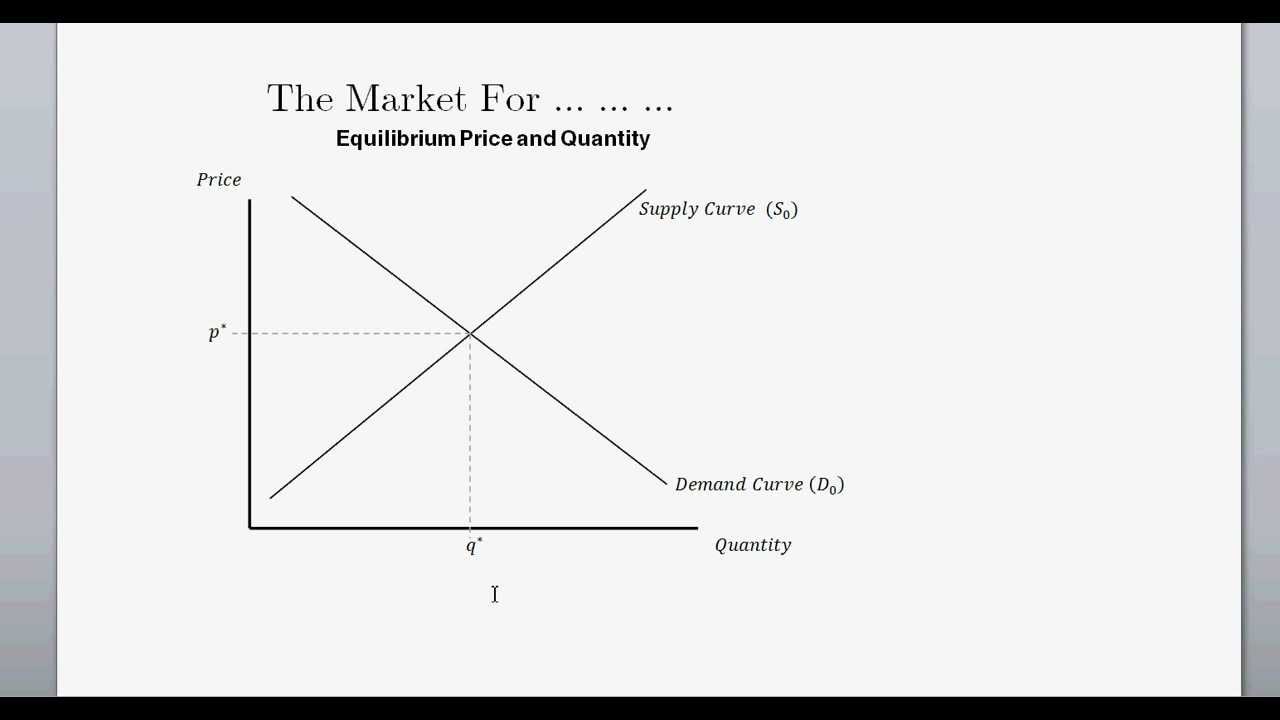 Supply And Demand And Equilibrium Price Quanitity Intro To Microeconomics
Supply And Demand And Equilibrium Price Quanitity Intro To Microeconomics
Introduction To Macroeconomics 3 Microeconomic Laws Of
Demand And Supply The Equilibrium Price And Quantity

0 Response to "On A Supply And Demand Diagram Quantity Demanded Equals Quantity Supplied"
Post a Comment