Given The Cost Curves In The Diagram What Market Situation Would You Expect To Occur
In this situation the total number of firms in the market would be three. Is the same as a price taking firm.
 Equilibrium Under Perfect Competition Perfectly Competitive
Equilibrium Under Perfect Competition Perfectly Competitive
In a perfectly competitive market the market supply curve reflects the sum of the marginal cost mc curves of firms in that industry.
Given the cost curves in the diagram what market situation would you expect to occur. Downward sloping and always equal to price. The market supply curve slopes upward the market demand curve slopes downward and the equilibrium rental price equals 350. Which curve has there been a movement of price and quantity.
Therefore the market demand curve that the oligopolist actually faces is the kinkeddemand curve labeled abc. Given this information and your answer in part a what is the firms profit maximizing level of production total revenue total cost and profit at this market equilibrium. The increase in price results in a movement along the supply curve resulting in an increase in quantity supplied.
Return to figure 3 a where the bottom of the long run average cost curve is at 10000 but now imagine that the total quantity of dishwashers demanded in the market at that price of 500 is only 30000. Assuming all factors are variable the long run average cost curve shows the minimum average cost of producing any given level of output. Indicate how each of the following events will have an effect on the market clear price and on the demand curve faced by the individual rental store.
The two market demand curves intersect at point b. Monopoly might experience economies of scale not available to the competitive firm. In a perfectly competitive market the market demand curve is downward sloping but the individual firm s demand curve is horizontal at the market price pe.
The market demand curve will shift to the right by 5 units at every price. The demand curve of the monopolist a. Competitive firms and markets we have learned the production function and cost function the question now is.
How much to produce such that firm can maximize his profit. Given the cost curves in the diagram what market situation would you expect to occur. The costs of a purely competitive firm and a monopoly could be different because the.
To solve this question firm has to make sure he can sell all he produces. Is the same as the industry demand curve. The firms mc equation based upon its tc equation is mc 2q 1.
It is obtained by combining all possible plant sizes. But this really depends on the demand curve and its belied. Given this new demand curve the new equilibrium will be approximately 350 and 17 units.
Micro eco chapter 23 24 25. Similarly the marginal revenue that the oligopolist actually receives is represented by the marginal revenue curve labeled adef. Horizontal just like for the perfectly competitive firm.
Market demand curve or the market supply curve you get p 400. The long run average cost curve is obtained by combining the possible short run curves ie. Is this a short run or long run equilibrium.
Marginal revenue for a monopolist is a.
 How To Calculate Marginal Cost 11 Steps With Pictures
How To Calculate Marginal Cost 11 Steps With Pictures
 Long Run Supply Curve In Constant Cost Perfectly Competitive Markets
Long Run Supply Curve In Constant Cost Perfectly Competitive Markets
Pricing Under Monopolistic And Oligopolistic Competition Jbdon
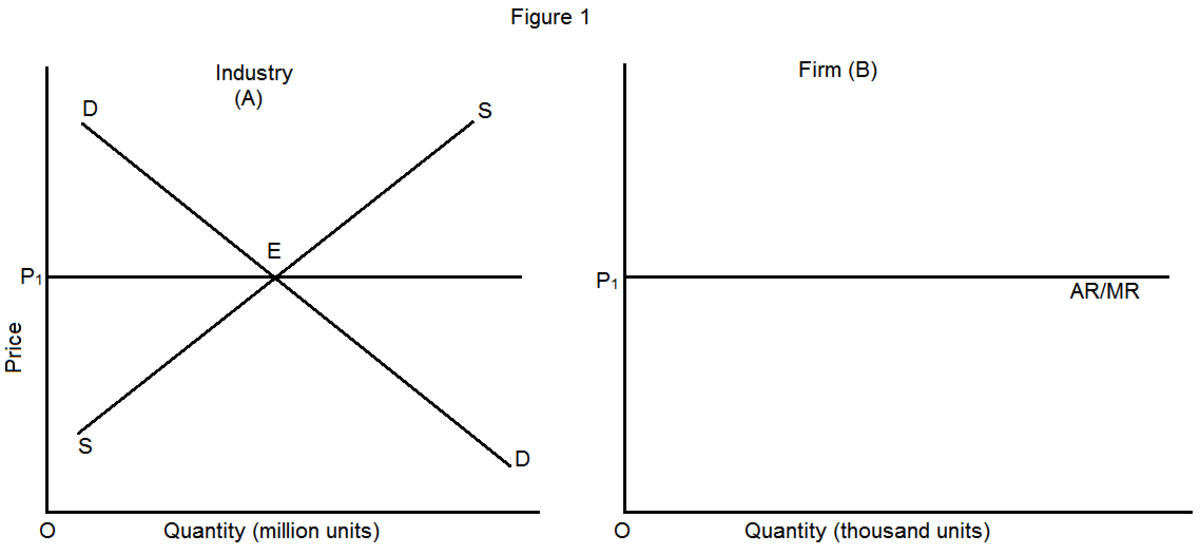 Relationship Between Average And Marginal Revenue Curves
Relationship Between Average And Marginal Revenue Curves
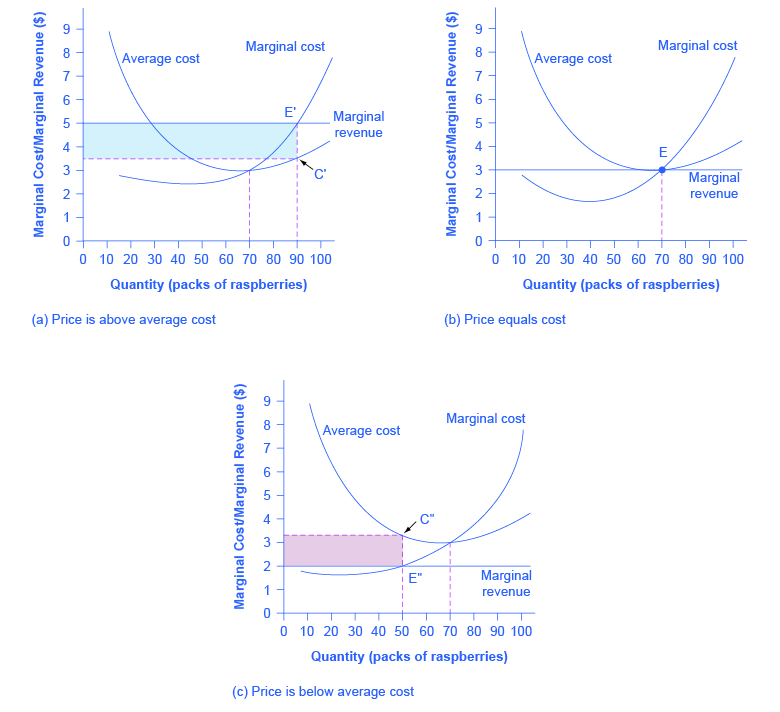
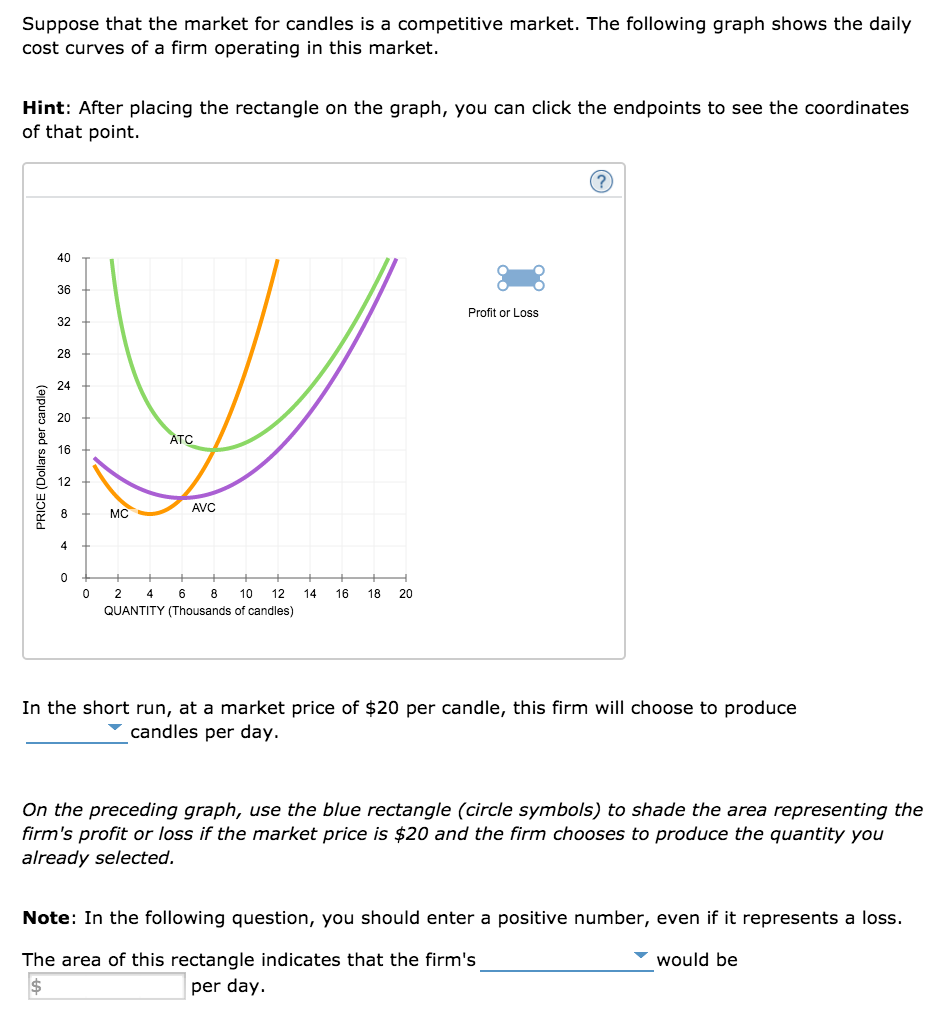 Solved Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Supp
Solved Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Supp
 Explaining Natural Monopoly Economics Tutor2u
Explaining Natural Monopoly Economics Tutor2u
Cost Of Production And Price Over Long And Short Periods
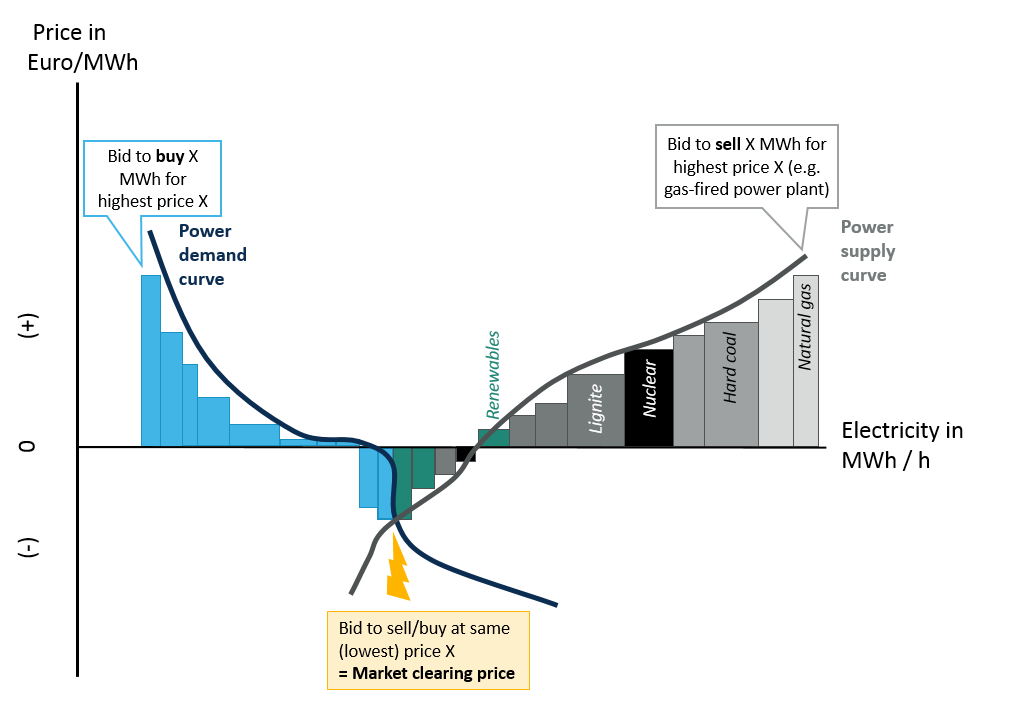 The Causes And Effects Of Negative Power Prices Clean
The Causes And Effects Of Negative Power Prices Clean

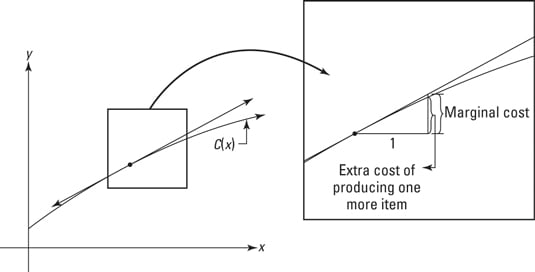 How To Determine Marginal Cost Marginal Revenue And
How To Determine Marginal Cost Marginal Revenue And
 8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions
8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions
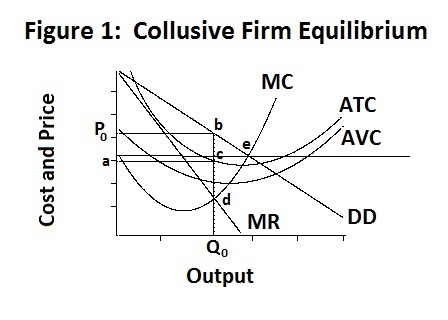 Duopoly Cournot Nash Equiibrium
Duopoly Cournot Nash Equiibrium

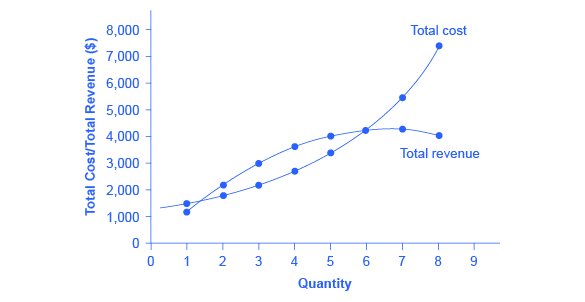 9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And
9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And
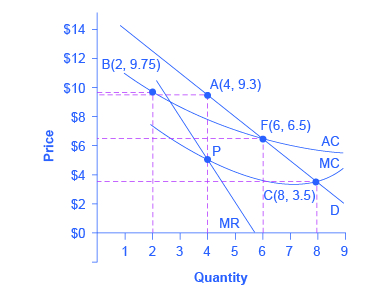 11 3 Regulating Natural Monopolies Principles Of Economics
11 3 Regulating Natural Monopolies Principles Of Economics
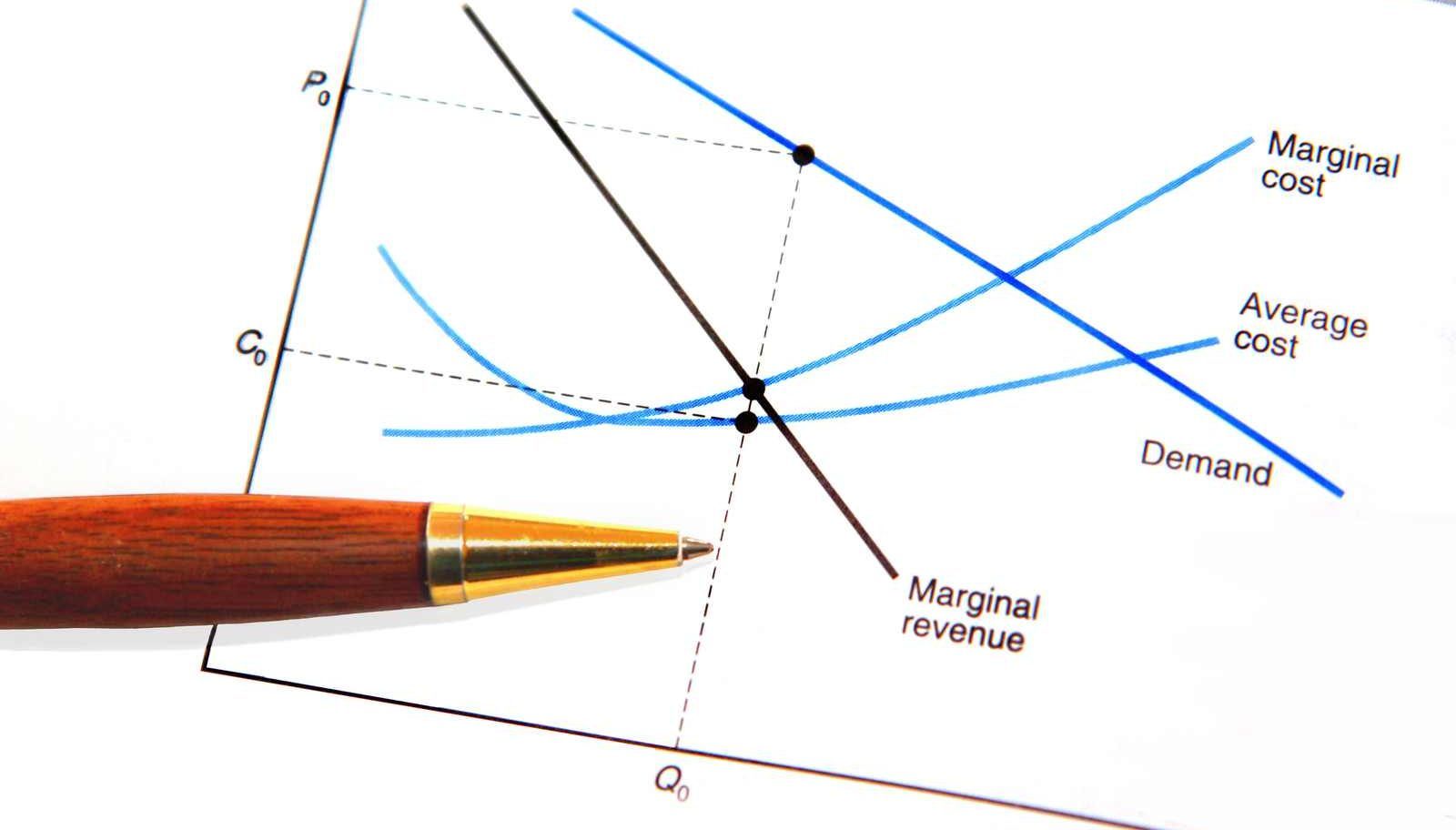 Marginal Cost Formula Definition Examples Calculate
Marginal Cost Formula Definition Examples Calculate
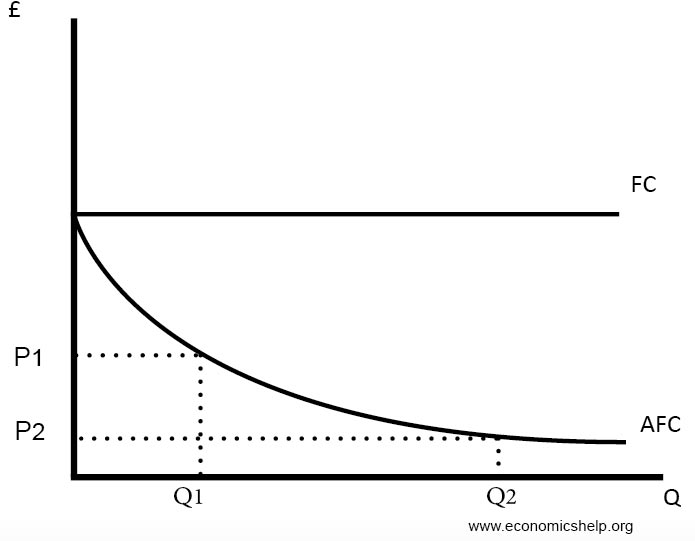 Diagrams Of Cost Curves Economics Help
Diagrams Of Cost Curves Economics Help
 Factor Markets Worked Example Video Khan Academy
Factor Markets Worked Example Video Khan Academy
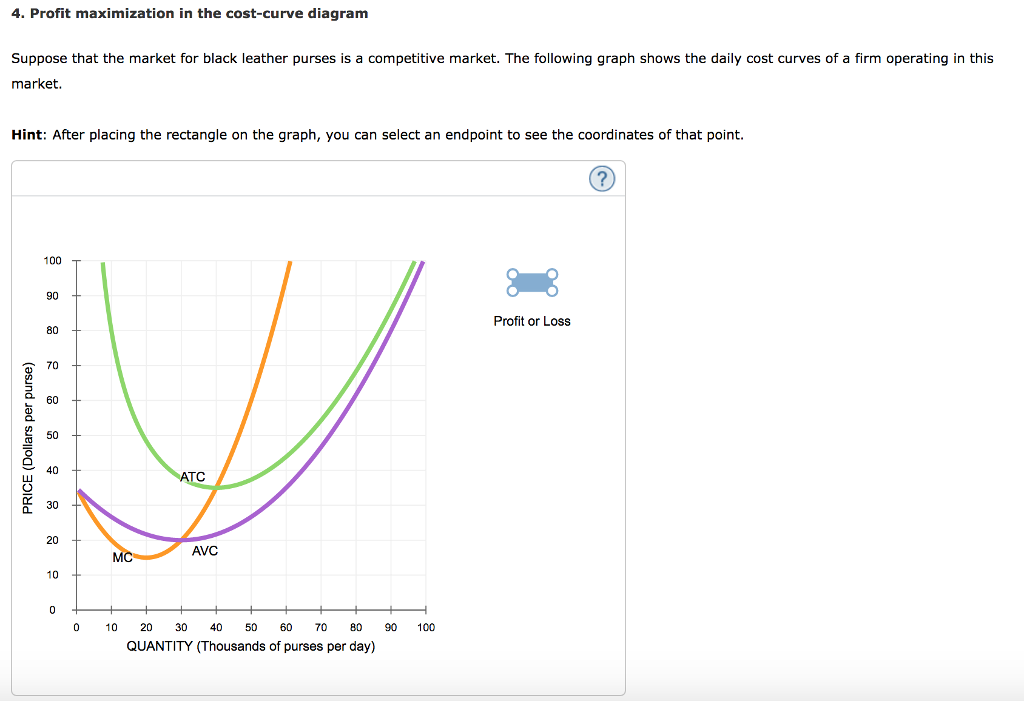 Solved 4 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram S
Solved 4 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram S
 Stock Market Forecast For 2019 7 Critical Trends To Watch
Stock Market Forecast For 2019 7 Critical Trends To Watch

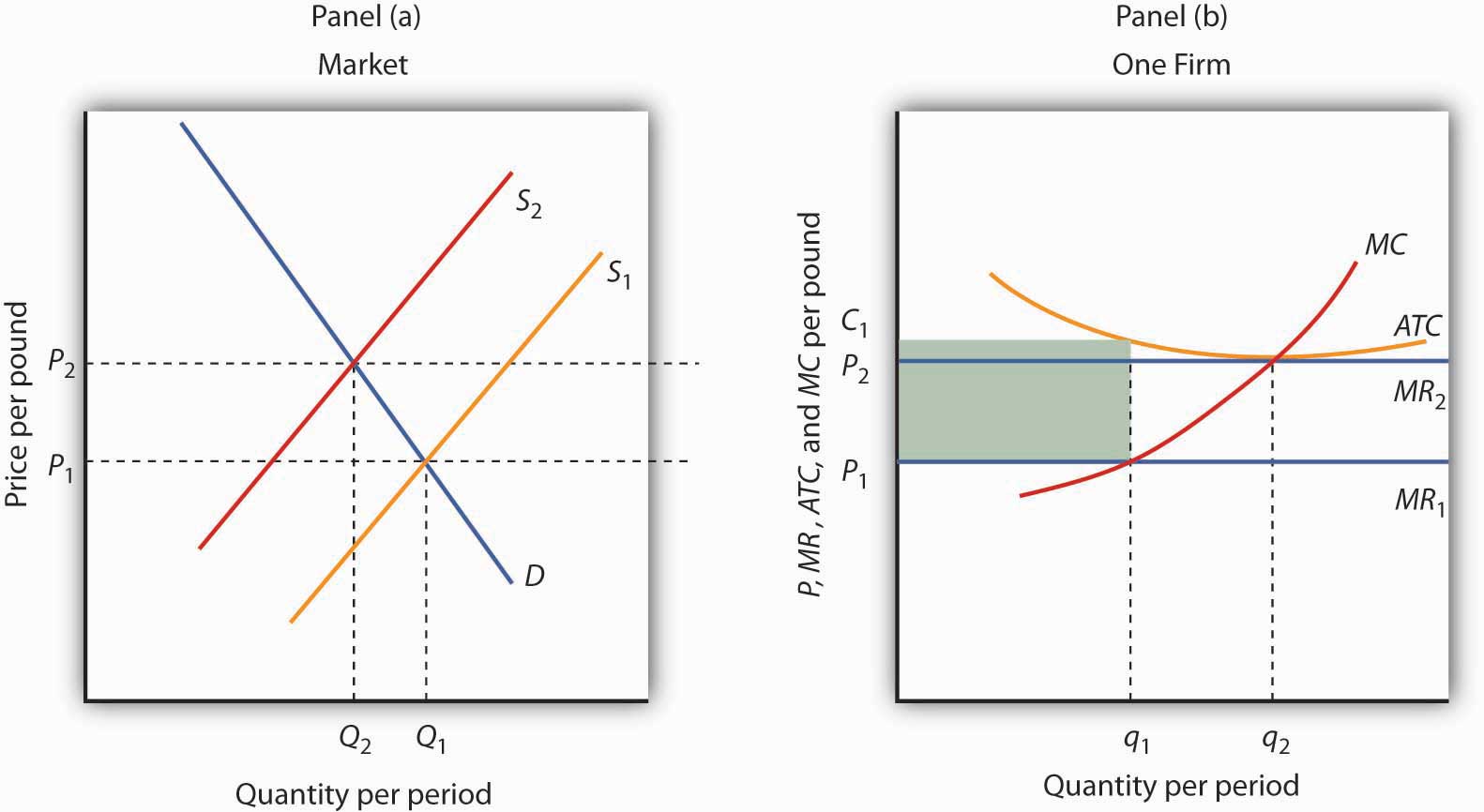 Perfect Competition In The Long Run
Perfect Competition In The Long Run
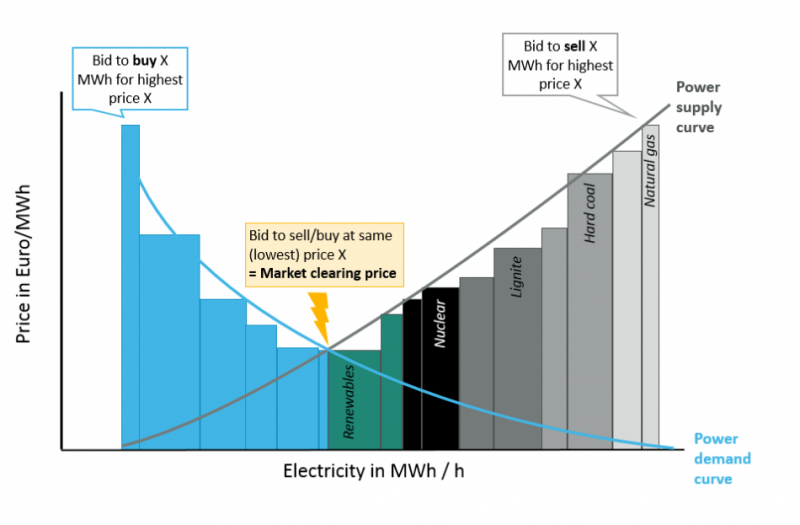 The Causes And Effects Of Negative Power Prices Clean
The Causes And Effects Of Negative Power Prices Clean
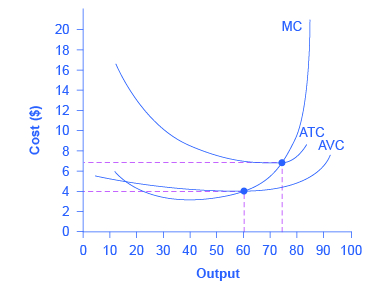
 Shale Cost Reductions Are 10 Technology And 90 Industry Bust
Shale Cost Reductions Are 10 Technology And 90 Industry Bust
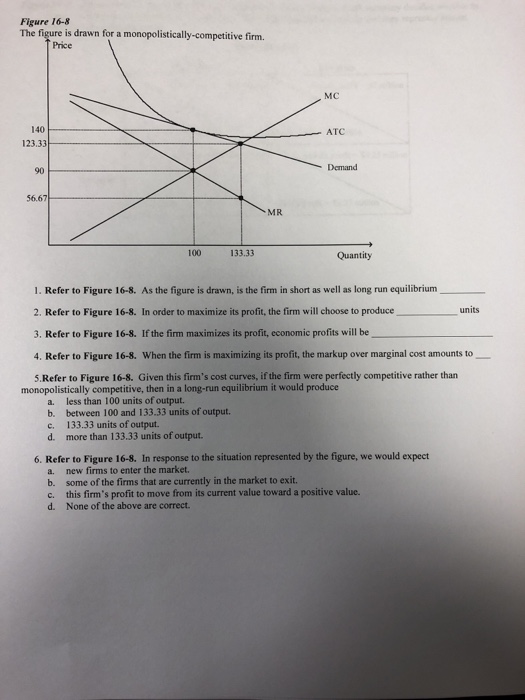

0 Response to "Given The Cost Curves In The Diagram What Market Situation Would You Expect To Occur"
Post a Comment