Refer To The Diagram For A Monopolistically Competitive Firm Long Run Equilibrium Price Will Be
If average total cost is below the market price then the firm will earn an economic profit. The short run equilibrium with profits and short run equilibrium with losses of a monopolistically competitive firm are explained with the help of two separate diagrams as under.
Monopolistic Competition In This Chapter You Will Pdf
When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long run equilibrium.

Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm long run equilibrium price will be. Note that a monopolistically competitive firm always operates somewhere to the left of the minimum point of its ac curve. Price competition can lead to lower economic profit or even loss. Production takes place where atc is minimized.
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Minimizing losses in the long run. The profit maximizing output for this firm will be.
2refer to the diagram. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. At p1 this firm will produce.
In short run equilibrium the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price. Long run equilibrium output will be. A rising marginal costs.
Long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where economic profits are zero results from. In the short run a monopolistically competitive firm maximizes profit or minimizes losses by producing that quantity that corresponds to when marginal revenue marginal cost. Monopolistically competitive firms frequently prefer nonprice to price competition because.
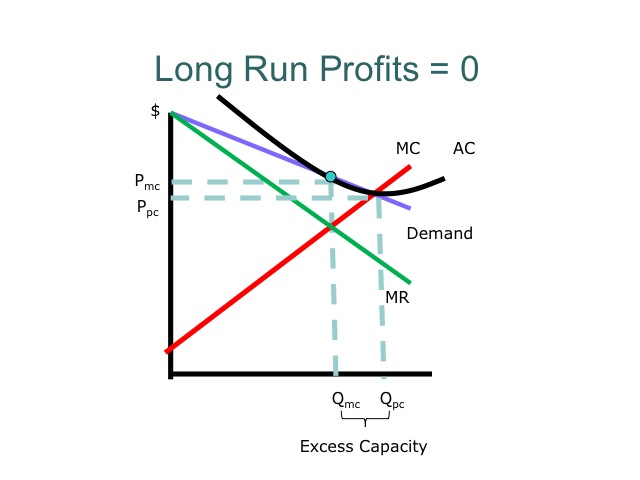
Minimizing losses in the short run. Marginal revenue equals marginal cost and price equals average total cost. In monopolistically competitive industries economic profits are competed away in the long run.
Hence there is no valid reason to criticize the performance and efficiency of such industries. About to leave the industry. Monopolistic competition in the long run.
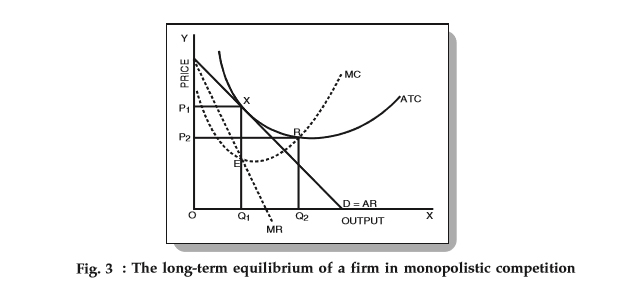
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically. The equilibrium output thus determined is oq m. In the figure 171 the downward sloping demand curve ar curve is quite elastic.
The firm gets normal profit by selling oq m output at the price op m. Realizing a normal profit in the long run. Long run equilibrium is achieved at point e where lmc equals mr fig.
If more firms would enter the industry and product differentiation would weaken. Normal profit is zero and price equals marginal cost. At this point the firms economic profits are zero and there is no longer any incentive for new firms to enter the market.
3refer to the diagram above. Thus in the longrun the competition brought about by the entry of new firms will cause each firm in a monopolistically competitive market to earn normal profits just like a perfectly competitive firm. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium.
At this output ar equals ac. 1refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm.
 13 Monopolistic Competition Ppt Video Online Download
13 Monopolistic Competition Ppt Video Online Download
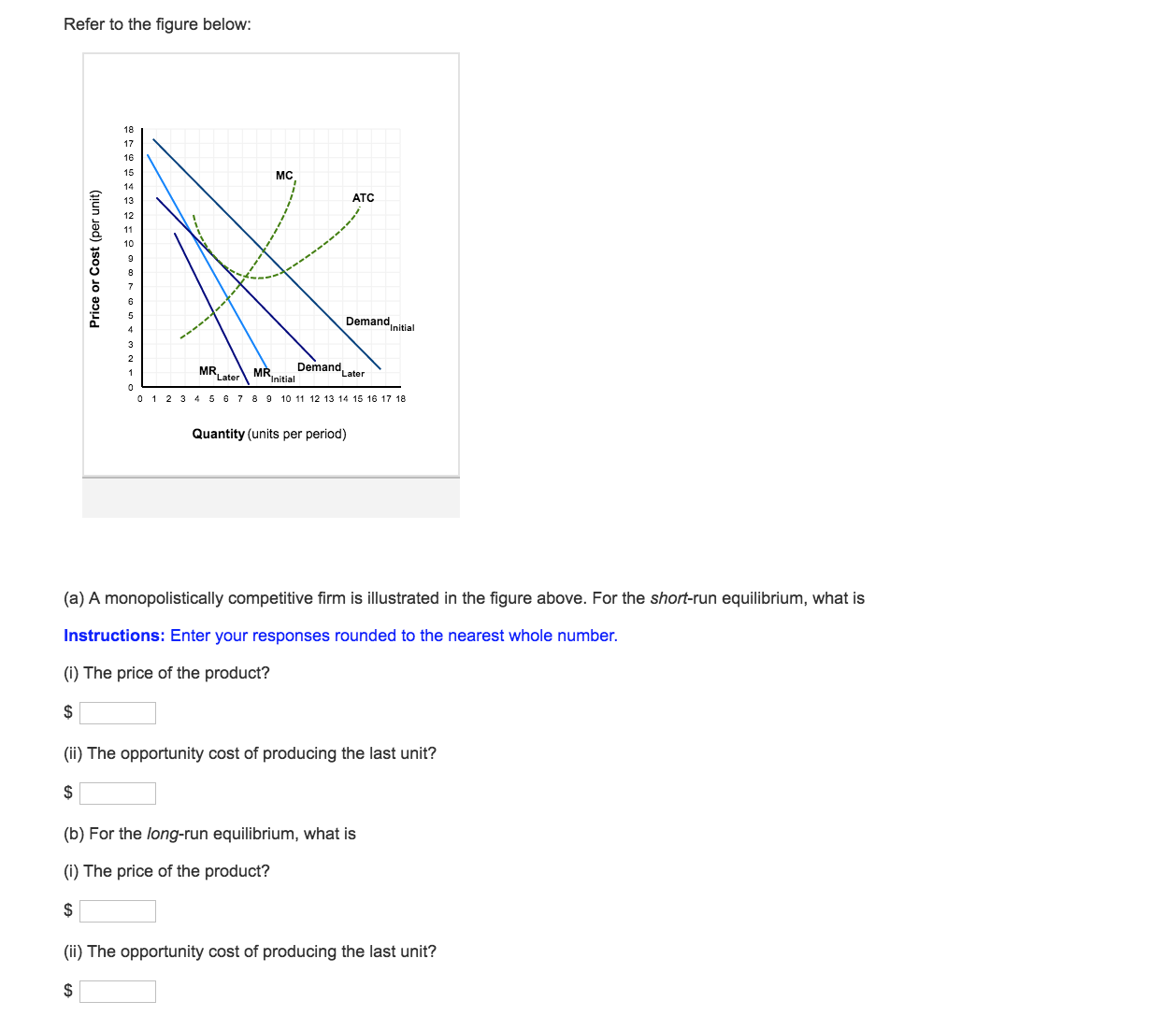 Solved Refer To The Figure Below A Monopolistically Comp
Solved Refer To The Figure Below A Monopolistically Comp
 2 Profit Maximization Of A Seller In A Monopolistically
2 Profit Maximization Of A Seller In A Monopolistically
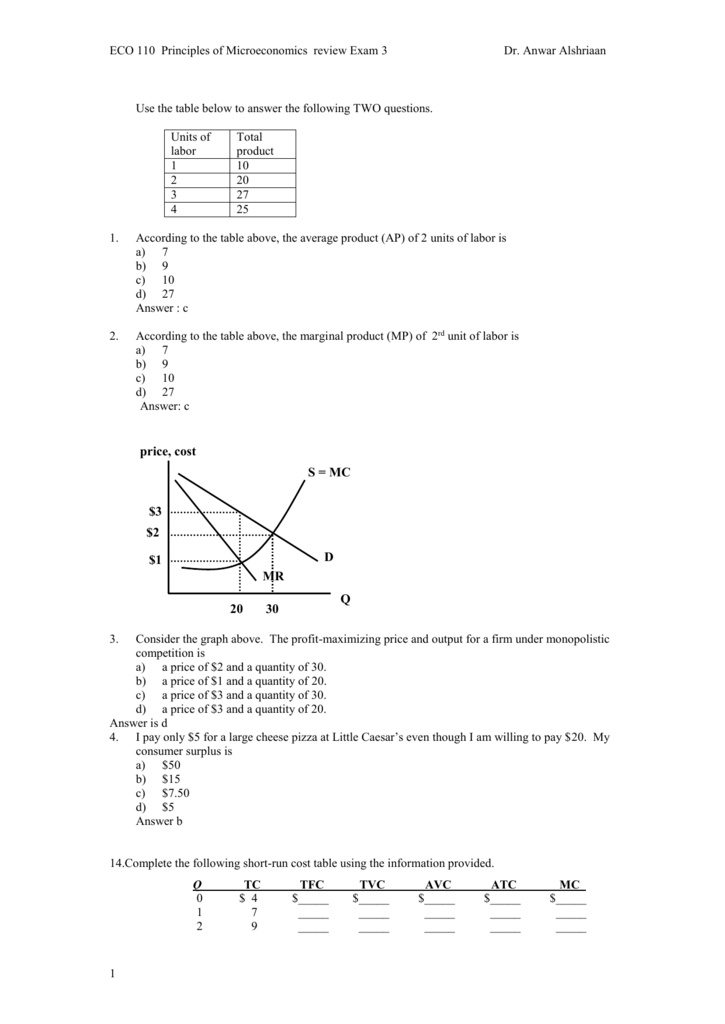 Use The Table Below To Answer The Following Two Questions
Use The Table Below To Answer The Following Two Questions
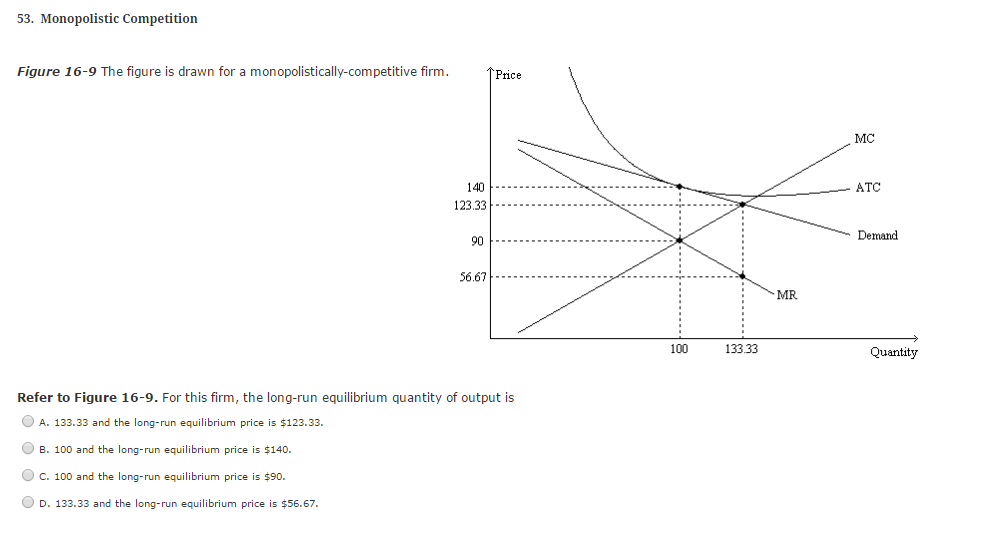 Solved 53 Monopolistic Competition Figure 16 9 The Figur
Solved 53 Monopolistic Competition Figure 16 9 The Figur
13monopolistic Competition And Oligopoly
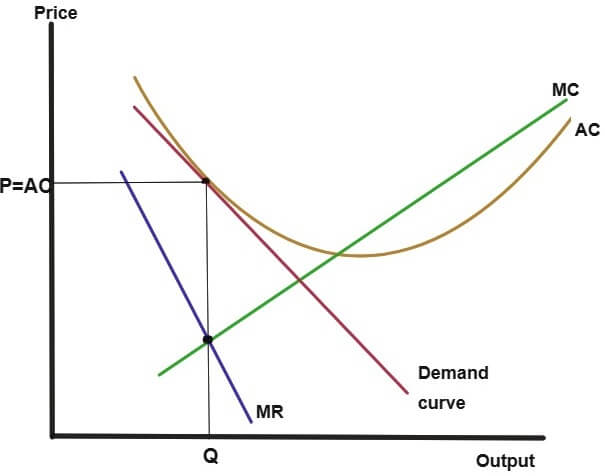 Monopolistic Competition Assignment Help Economics
Monopolistic Competition Assignment Help Economics
 Refer To The Above Diagrams Which Pertain To
Refer To The Above Diagrams Which Pertain To
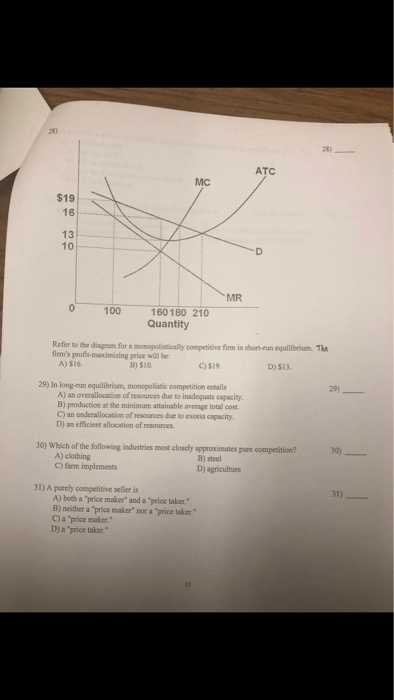 Solved Z8 28 Atc Mc 19 16 13 10 Mr 160180 210 Quantity
Solved Z8 28 Atc Mc 19 16 13 10 Mr 160180 210 Quantity
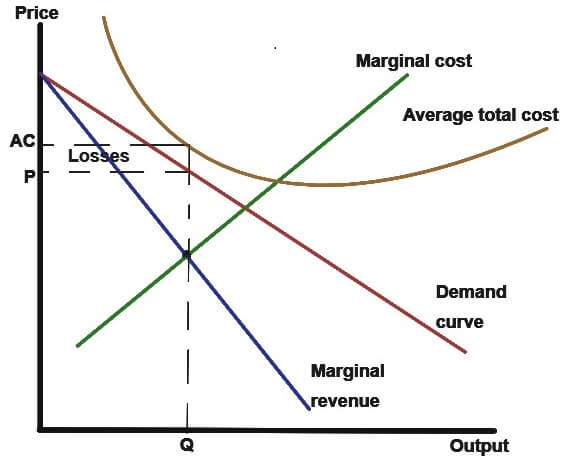 Monopolistic Competition Assignment Help Economics
Monopolistic Competition Assignment Help Economics
 In The Long Run The Price Charged By A Monopolistically
In The Long Run The Price Charged By A Monopolistically


Chapter 11 Monopolistic Becn150 Macroeconomics Studocu
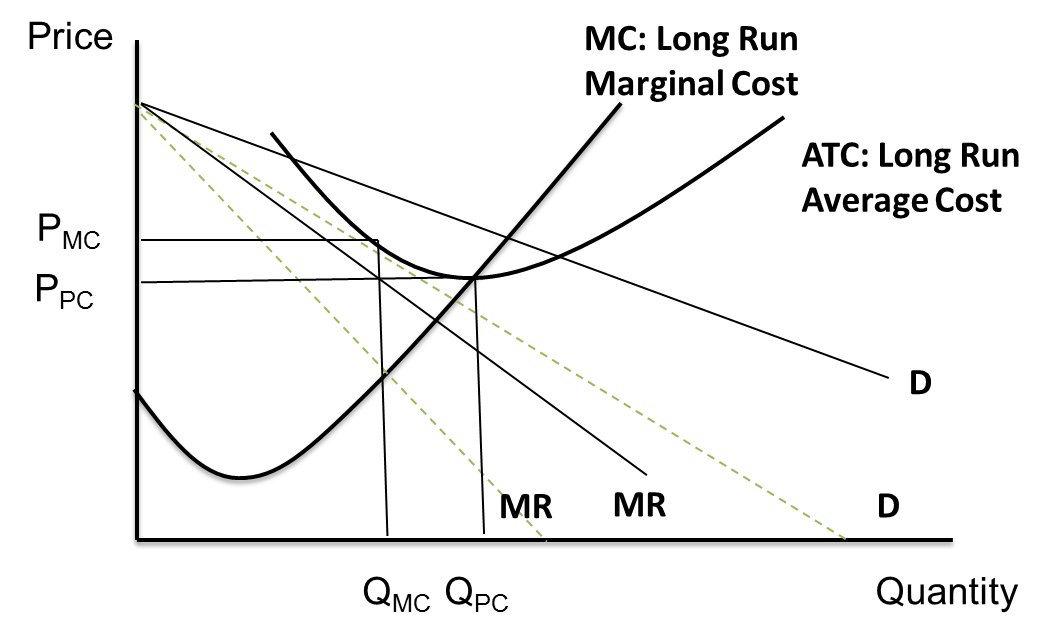 4 4 Factors Affecting Long Run Equilibrium In
4 4 Factors Affecting Long Run Equilibrium In
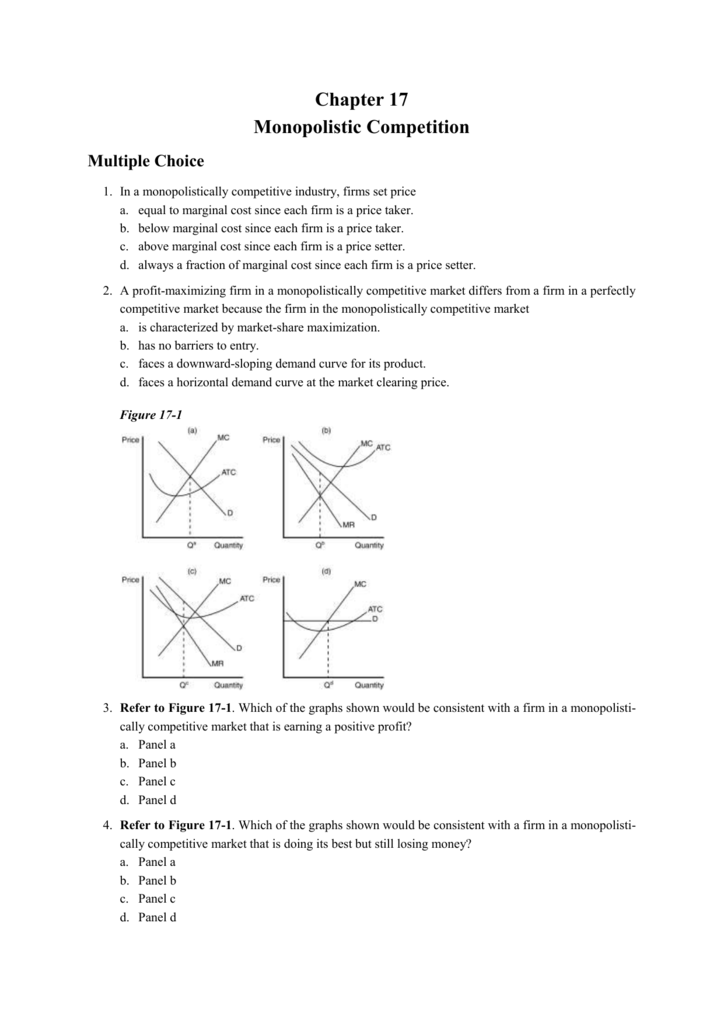 Chapter 17 Mc Monopolistic Competition
Chapter 17 Mc Monopolistic Competition
 Microeconomics Chapter 11 Monopolistic Macroeconomics 2013
Microeconomics Chapter 11 Monopolistic Macroeconomics 2013

 Quiz 7 Review Review Test Submission Quiz 07 Question1
Quiz 7 Review Review Test Submission Quiz 07 Question1
 Monopolistic Competition Features Price Determination
Monopolistic Competition Features Price Determination
 8 4 Monopolistic Competition Principles Of Microeconomics
8 4 Monopolistic Competition Principles Of Microeconomics
 Microeconomics Chapter 11 Monopolistic Macroeconomics 2013
Microeconomics Chapter 11 Monopolistic Macroeconomics 2013
13monopolistic Competition And Oligopoly
Solved Information Answer The Following Questions On The
 Equilibrium Under Monopolistic Competition Group
Equilibrium Under Monopolistic Competition Group
 Economics Lecture Notes Chapter 6 Economics Cafe
Economics Lecture Notes Chapter 6 Economics Cafe

0 Response to "Refer To The Diagram For A Monopolistically Competitive Firm Long Run Equilibrium Price Will Be"
Post a Comment